Permission groups in SchoolMind have different levels. These levels determine what permission groups a user can assign to other users. Administrator permission group is of the highest level (level 1) while other permission groups are of a lower level (level 2, level 3, etc). The higher the number - the lower the level.
Example:
| Name | Level |
|---|---|
| Administrator Permission Group | 1 |
| Principal Permission Group | 2 |
| Vice-Principal Permission Group | 3 |
Considering the example above, if the user is a member of the level 1 permission group, the user should be able to see all groups when assigning a group to other users.
If the user has permission that has is level 2, the user will see only groups that are greater or equal to level 2 permission groups.
Notes:
- Administrator permission group is level 1 by default and cannot be changed.
- No other permission group can be of level 1 which is reserved for Administrator.
- If the user a member of level 1 permission group in institution A, and member of level 2 permission group in institution B, in institution B the user can only see or assign users to permission groups of level 2 or lower (level 3, level 4, etc).
So shortly, permission group levels determine what permission groups a user can assign to another user (if he has the required permission) and also make sure users can't assign themselves as administrators in the system.
Permission group levels can be set in the System module and should be defined by the SchoolMind admin. To do so:
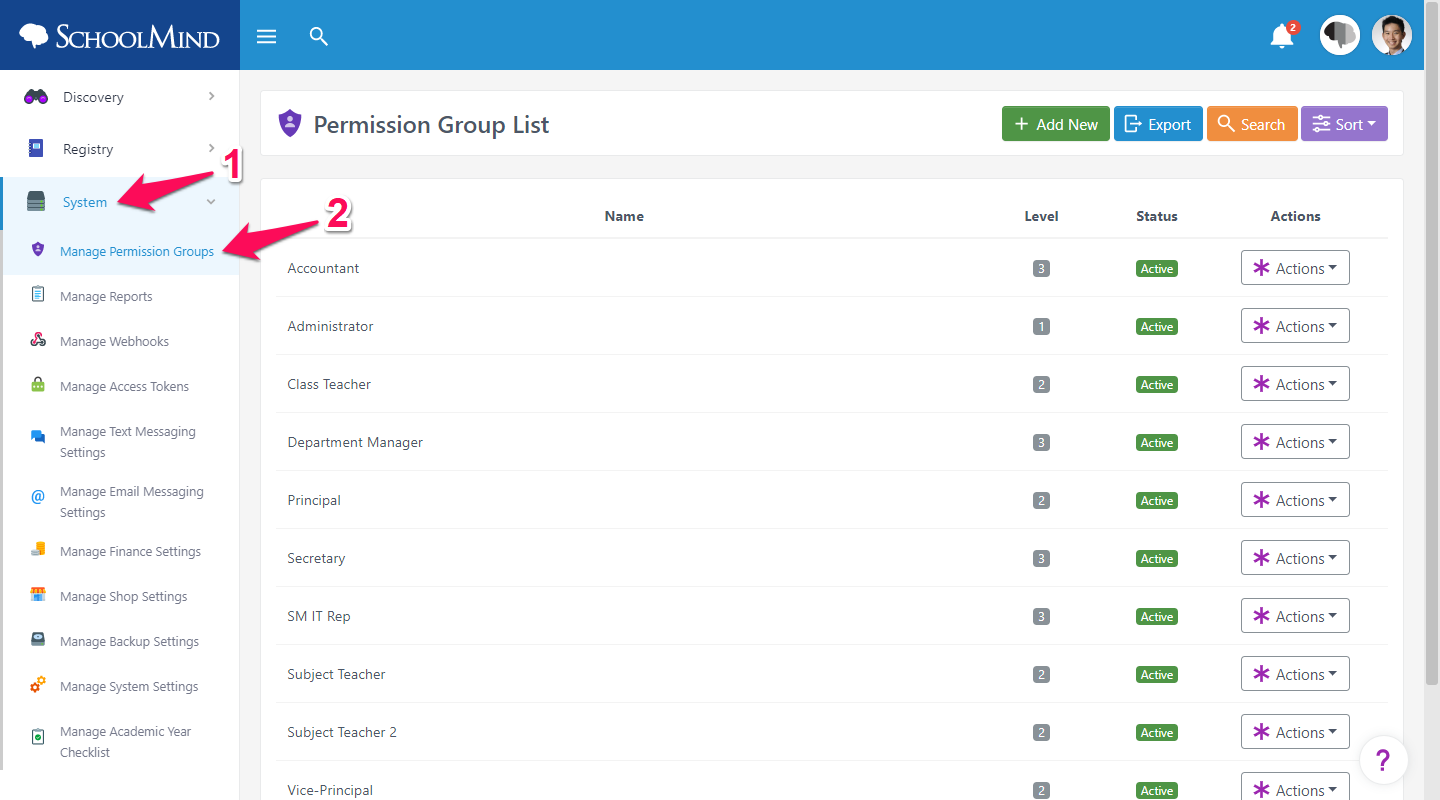
1. Navigate to System > Manage Permission Groups.
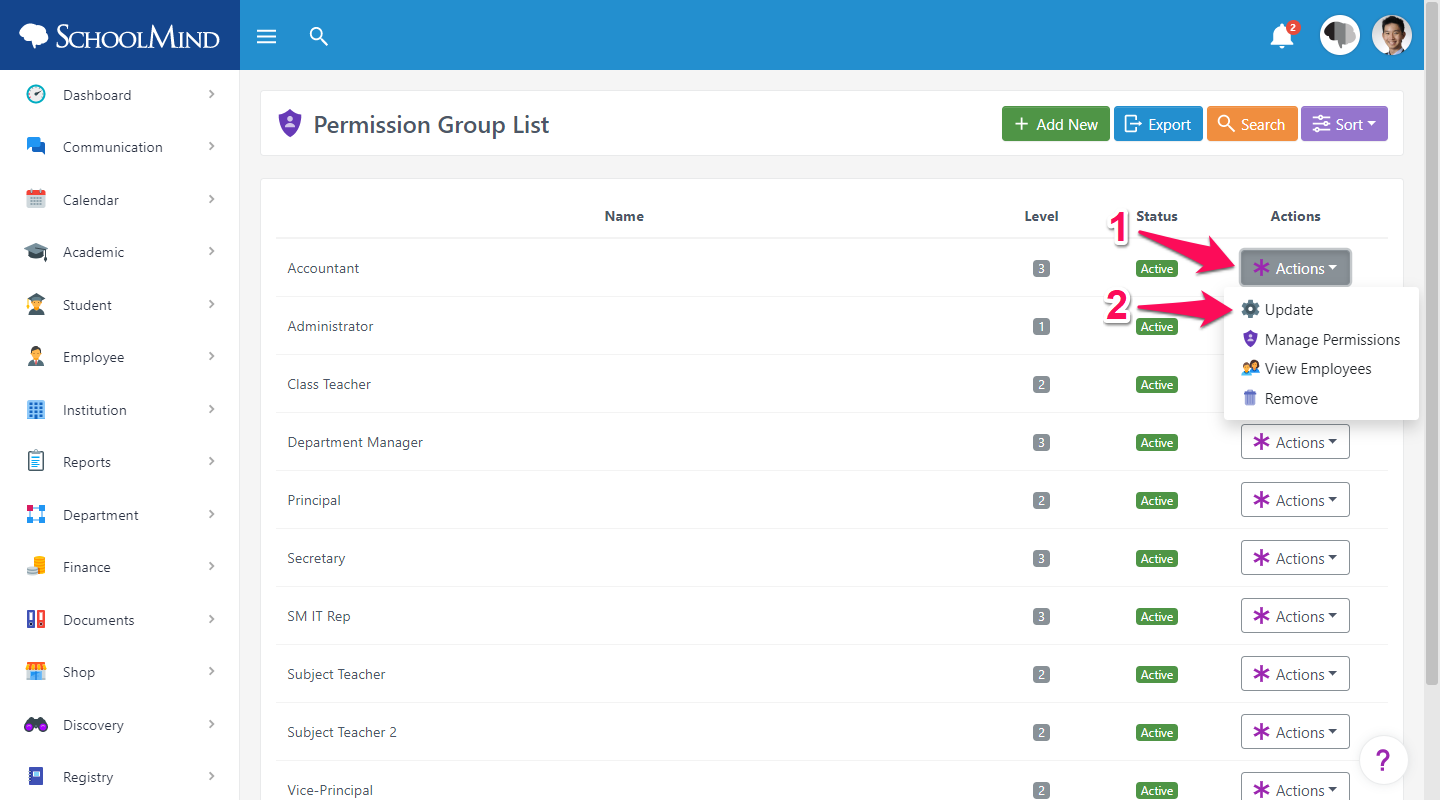
2. Choose a permission group from the list and click Actions > Update.
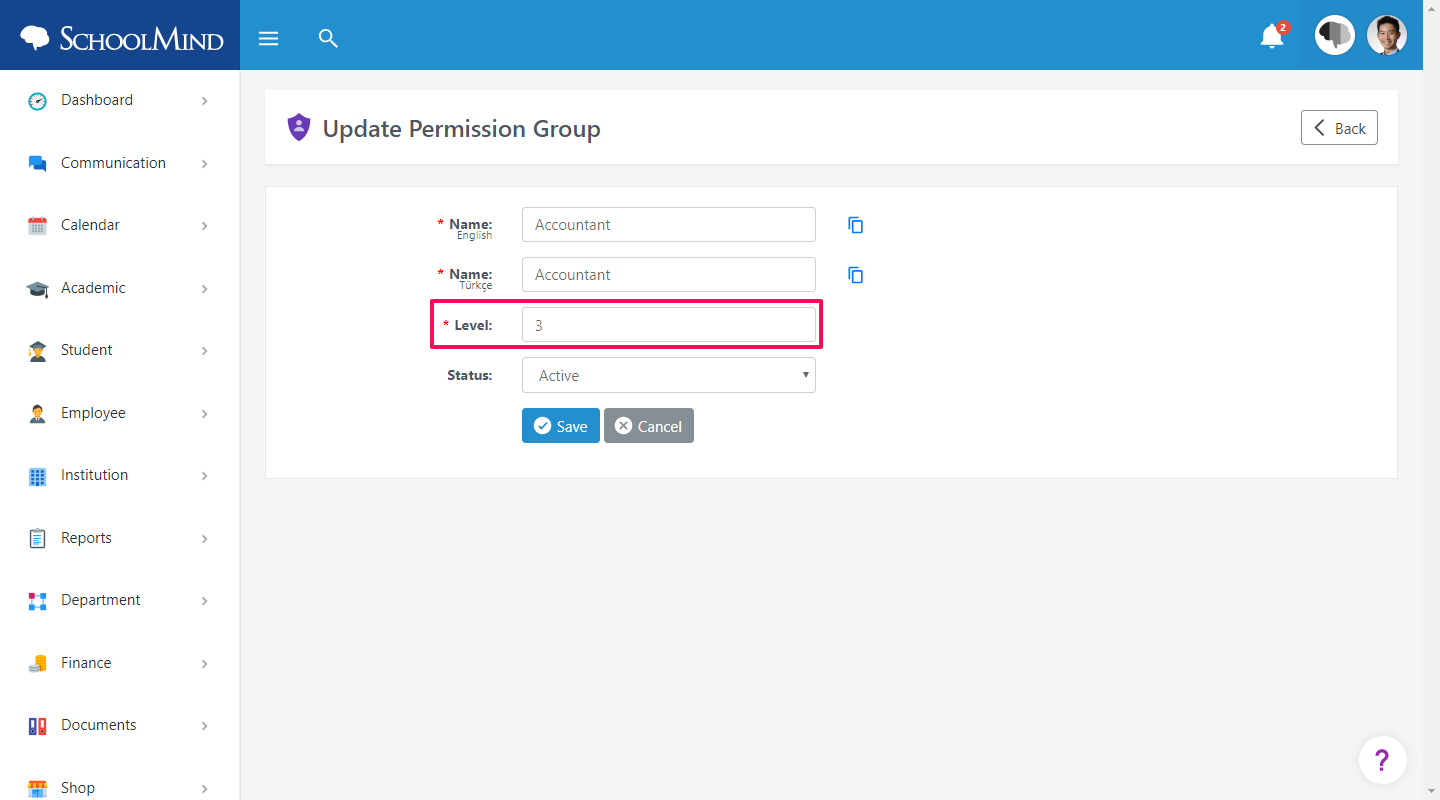
3. Set the level for the permission group according to your policy and click Save.
4. Do the same for all other permission groups.
Example:
Once you have set levels for all permission groups users which are members of a permission group of a lower level, won't be able to assign users to permission groups of a higher level.
<p class="sm-help-tag">sm_help_admin_system_manage_permission_groups</p>


Comments
0 comments
Article is closed for comments.